💗个人主页💗
⭐个人专栏——数据结构学习⭐
💫点击关注🤩一起学习C语言💯💫
目录
导读:1. vim 指令2. head指令3. tail指令4. tree指令5. 输出重定向6. echo指令7. wc指令8. | 字符9. date指令10. Cal指令11. find指令12. grep指令13. zip/unzip指令14. tar指令15. bc指令16. uname –r指令17. 热键18. shutdown
导读:
前面我们在Linux基本指令(一)学习了ls,pwd,cd,touch,mkdir,rmdir,rm,man,cp,mv,cat,more,less指令。
今天我们学习的指令有vim,head,tail,tree,echo,wc,|,date,cal,find,grep,zip&&unzip,tar,bc,uname -r,shutdown。
1. vim 指令
vim是一款功能强大的文本编辑器,它在Linux系统中被广泛使用。
打开一个文件:
vim filename
切换到插入模式以编辑文件:
按下i键或者a键进入插入模式,然后开始编辑文件。
保存文件并退出:
Ecs键+Shift键+: ,输入wq,然后按下回车键。
不保存文件并退出:
Ecs键+Shift键+: ,输入q!,然后按下回车键。
以上只是vim编辑器的一些基本操作,vim还有很多高级功能和编辑技巧。您可以通过查阅vim的帮助文档或者在线教程来学习更多关于vim的用法。
[zhy@Centos ~]$ vim file.txt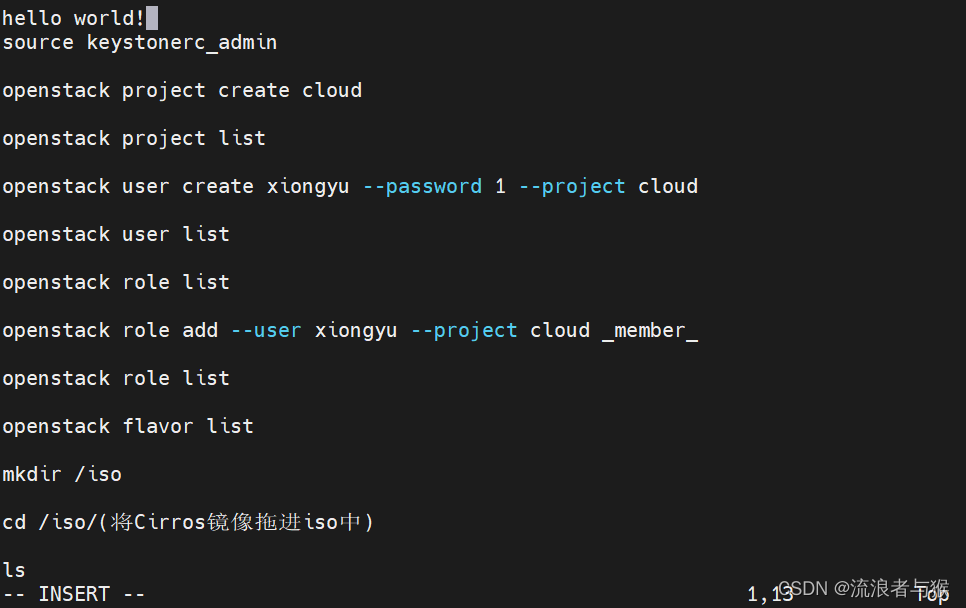
2. head指令
head指令用于显示文件的开头几行,默认显示文件的前10行。
语法:
head [选项][文件]
常用选项:
-n NUM:显示文件的前NUM行,默认为10行。
-c NUM:显示文件的前NUM个字节。
-q:不显示文件名。
-v:总是显示文件名。
[zhy@Centos ~]$ head -c 100 file.txthello world!source keystonerc_adminopenstack project create cloudopenstack project listopenst#显示多个文件的前10行,并显示文件名:[zhy@Centos ~]$ head -v file.txt newfile.txt==> file.txt <==hello world!source keystonerc_adminopenstack project create cloudopenstack project listopenstack user create xiongyu --password 1 --project cloudopenstack user list==> newfile.txt <==hello world!wolf3. tail指令
相对于head指令显示文件的前10行,tail指令用于显示文件的末尾几行,默认显示文件的末尾10行。
语法:
tail [选项][文件]
常用选项:
-n NUM:显示文件的后NUM行,默认为10行。
-c NUM:显示文件的后NUM个字节。
-f:实时跟踪文件的变化,会不断更新显示文件的末尾内容。
#显示文件的后10行:[zhy@Centos ~]$ tail file.txtopenstack image create --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --min-disk 2 --min-ram 1024 --file /iso/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img Cirrosopenstack image listopenstack image set Cirros --publicopenstack network create GW --share --provider-network-type flat --provider-physical-network extent --project cloud --externalopenstack network list#显示文件的后5行:[zhy@Centos ~]$ tail -n 5 file.txtopenstack image set Cirros --publicopenstack network create GW --share --provider-network-type flat --provider-physical-network extent --project cloud --externalopenstack network list#显示文件的后100个字节:[zhy@Centos ~]$ tail -c 100 file.txtork-type flat --provider-physical-network extent --project cloud --externalopenstack network list#实时跟踪文件的末尾内容:[zhy@Centos ~]$ tail -f file.txtopenstack image create --container-format bare --disk-format qcow2 --min-disk 2 --min-ram 1024 --file /iso/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img Cirrosopenstack image listopenstack image set Cirros --publicopenstack network create GW --share --provider-network-type flat --provider-physical-network extent --project cloud --externalopenstack network list^C4. tree指令
tree指令用于以树状图形式显示目录结构。
语法:
tree [选项] [目录]
常用选项:
-a:显示所有文件和目录,包括隐藏文件。
-L n:限制显示的层级数为n。
-d:只显示目录。
-f:不显示目录,只显示文件。
-P pattern:只显示符合指定模式的文件和目录。
#显示当前目录的树状结构:[zhy@Centos ~]$ tree.├── 111│ ├── book│ └── tmp1├── file.txt├── newfile.txt├── test.txt├── tmp1│ ├── book│ └── file2.txt└── tmp2 ├── book └── tmp15 directories, 7 files5. 输出重定向
输出重定向是一种在命令行环境中将输出结果从标准输出(通常是显示器)转向到文件或其它设备的方法。在Linux系统中,使用特殊的符号>或>>来实现输出重定向。
>:将命令的标准输出重定向到一个文件中,并覆盖原有内容。如果文件不存在,则创建新文件。>>:将命令的标准输出追加到一个文件中,不覆盖原有内容。如果文件不存在,则创建新文件。下面我们用echo指令来演示一下。
6. echo指令
在Linux中,echo是一条非常常用的指令。它用于将文本或字符串输出到终端或文件。
语法:
echo [选项] [字符串]
#输出文字到终端:[zhy@Centos ~]$ echo Hello, World!Hello, World!#使用转义字符:[zhy@Centos ~]$ echo -e "Hello\nWorld!"HelloWorld!#将echo命令的输出结果覆盖到名为file.txt的文件中。[zhy@Centos ~]$ echo "Hello World!" > file.txt[zhy@Centos ~]$ cat file.txtHello World!#将输出追加到文件:[zhy@Centos ~]$ echo "Hello World!" >> file.txt[zhy@Centos ~]$ cat file.txtHello World!Hello World!7. wc指令
在Linux中,wc是一个用于统计文件中字节数、字数、行数的命令。
语法:
wc [选项][文件]
常用选项:
-c:统计文件中的字节数。
-w:统计文件中的字数(以空白字符分隔的单词)。
-l:统计文件中的行数。
[zhy@Centos ~]$ cat file.txtHello World!Hello World!#统计文件中的字节数、字数和行数:[zhy@Centos ~]$ wc file.txt 2 4 26 file.txt #只统计文件中的字节数:[zhy@Centos ~]$ wc -c file.txt26 file.txt#只统计文件中的字数:[zhy@Centos ~]$ wc -w file.txt4 file.txt#只统计文件中的行数:[zhy@Centos ~]$ wc -l file.txt2 file.txt8. | 字符
在Linux中,竖线符号(|)代表管道操作符(Pipe),用于将一个命令的输出作为另一个命令的输入。
通过使用管道操作符可以将多个命令串联起来,实现更复杂的数据处理任务。
语法:
command1 | command2
上述命令将command1的输出作为command2的输入。command1和command2可以是任意命令,它们可以是系统自带的命令,也可以是用户自定义的脚本或程序。
管道的优点是可以将多个简单的命令组合在一起,实现更复杂的操作。可以通过管道来过滤、排序、统计、转换数据,或者将多个命令的功能组合起来使用。
比如:
#使用cat命令读取文件内容,并通过管道将结果传递给wc命令统计文件的行数:[zhy@Centos ~]$ cat file.txt | wc -l29. date指令
Linux中,date用于显示和设置系统的日期和时间。
语法:
date [选项][格式]
常用选项:
-d, --date=STRING:指定要显示或设置的日期和时间字符串。
-u, --utc:显示或设置协调世界时(UTC)。
-s, --set=STRING:设置系统的日期和时间。
-R, --rfc-2822:以RFC 2822格式输出日期和时间。
–rfc-3339=TIMESPEC:以RFC 3339格式输出日期和时间。
#显示当前日期和时间:[zhy@Centos ~]$ dateThu Jan 4 07:53:19 PM CST 2024#以特定格式显示当前日期和时间:[zhy@Centos ~]$ date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"2024-01-04 19:53:36#显示指定日期和时间的格式化结果:[zhy@Centos ~]$ date -d "2022-01-01 12:00:00" "+%A, %B %d, %Y"Saturday, January 01, 202210. Cal指令
cal命令可以用来显示公历(阳历)日历。
语法:
cal [参数][月份][年份]
#显示当前月份的日历:[zhy@Centos ~]$ cal January 2024Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1314 15 16 17 18 19 2021 22 23 24 25 26 2728 29 30 31#显示指定年份的日历:[zhy@Centos ~]$ cal 2024 2024 January February MarchSu Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3 4 5 6 7 8 914 15 16 17 18 19 20 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 10 11 12 13 14 15 1621 22 23 24 25 26 27 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 17 18 19 20 21 22 2328 29 30 31 25 26 27 28 29 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 April May JuneSu Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 1 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 814 15 16 17 18 19 20 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 9 10 11 12 13 14 1521 22 23 24 25 26 27 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 16 17 18 19 20 21 2228 29 30 26 27 28 29 30 31 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 July August SeptemberSu Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 8 9 10 11 12 13 1414 15 16 17 18 19 20 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 15 16 17 18 19 20 2121 22 23 24 25 26 27 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 22 23 24 25 26 27 2828 29 30 31 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 29 30 October November DecemberSu Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 8 9 10 11 12 13 1413 14 15 16 17 18 19 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 15 16 17 18 19 20 2120 21 22 23 24 25 26 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 22 23 24 25 26 27 2827 28 29 30 31 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 29 30 31#显示指定月份和年份的日历:[zhy@Centos ~]$ cal 1 2024 January 2024Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1314 15 16 17 18 19 2021 22 23 24 25 26 2728 29 30 31# 显示当月与前后月份的日历:[zhy@Centos ~]$ cal -3 December 2023 January 2024 February 2024Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 4 5 6 7 8 9 1010 11 12 13 14 15 16 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 11 12 13 14 15 16 1717 18 19 20 21 22 23 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 18 19 20 21 22 23 2424 25 26 27 28 29 30 28 29 30 31 25 26 27 28 293111. find指令
Find是一个强大的Linux命令行工具,用于在文件系统中查找文件和目录。它可以按照多种条件进行搜索,并可以执行各种操作。
语法:
find pathname -options
[zhy@Centos ~]$ find /home/zhy/tmp1/file2.txt/home/zhy/tmp1/file2.txt12. grep指令
grep是一个在Linux和Unix系统中用于查找文件中匹配文本模式的强大命令行工具。它可以从一个或多个文件中搜索匹配的行,并将结果输出到标准输出。
语法:
grep [pattern] [files]
常用选项:
-i :忽略大小写的不同,所以大小写视为相同
-n :顺便输出行号
-v :反向选择,亦即显示出没有 ‘搜寻字符串’ 内容的那一行
#基本搜索[zhy@Centos ~]$ grep 'l' file.txtHello World!Hello World!#忽略大小写搜索:[zhy@Centos ~]$ grep 'h' file.txt[zhy@Centos ~]$ grep -i 'h' file.txtHello World!Hello World!13. zip/unzip指令
在Linux中,可以使用zip和unzip命令来压缩和解压缩文件。
语法:
zip <压缩文件名>.zip <文件或目录>
[zhy@Centos ~]$ tree.├── 111│ ├── book│ └── tmp1├── file.txt├── newfile.txt├── test.txt├── tmp1│ ├── book│ └── file2.txt└── tmp2 ├── book └── tmp15 directories, 7 files#压缩文件[zhy@Centos ~]$ zip tmp3.zip newfile.txt adding: newfile.txt (stored 0%)[zhy@Centos ~]$ tree.├── 111│ ├── book│ └── tmp1├── file.txt├── newfile.txt├── test.txt├── tmp1│ ├── book│ └── file2.txt├── tmp2│ ├── book│ └── tmp1└── tmp3.zip5 directories, 8 files# 解压文件[zhy@Centos ~]$ unzip tmp3.zipArchive: tmp3.zipreplace newfile.txt? [y]es, [n]o, [A]ll, [N]one, [r]ename: y extracting: newfile.txt[zhy@Centos ~]$ tree.├── 111│ ├── book│ └── tmp1├── file.txt├── newfile.txt├── test.txt├── tmp1│ ├── book│ └── file2.txt├── tmp2│ ├── book│ └── tmp1└── tmp3.zip5 directories, 8 files14. tar指令
在Linux中,tar是一个常用的命令行工具,用于创建和提取归档文件,也称为"tarball"。
语法:
打包:
tar -cvf <归档文件名>.tar <文件或目录>
解包:
tar -xvf <归档文件名>.tar
常用选项:
-c :建立一个压缩文件的参数指令(create 的意思);
-x :解开一个压缩文件的参数指令!
-t :查看 tarfile 里面的文件!
-z :是否同时具有 gzip 的属性?亦即是否需要用 gzip 压缩?
-j :是否同时具有 bzip2
的属性?亦即是否需要用 bzip2 压缩?
-v :压缩的过程中显示文件!这个常用,但不建议用在背景执行过程!
-f :使用档名,请留意,在 f之后要立即接档名!不要再加参数!
-C : 解压到指定目录
#打包[zhy@Centos ~]$ tar -cvf tmp4.tar /home/zhy/tmp2tar: Removing leading `/' from member names/home/zhy/tmp2//home/zhy/tmp2/tmp1//home/zhy/tmp2/book[zhy@Centos ~]$ lltotal 40drwxrwxr-x 3 zhy zhy 4096 Jan 2 20:25 111-rw-rw-r-- 1 zhy zhy 26 Jan 4 19:12 file.txt-rw-rw-r-- 1 zhy zhy 18 Jan 3 19:27 newfile.txt-rw-rw-r-- 1 zhy zhy 5 Jan 3 19:23 test.txtdrwxrwxr-x 2 zhy zhy 4096 Jan 3 19:12 tmp1drwxrwxr-x 3 zhy zhy 4096 Jan 3 18:46 tmp2-rw-rw-r-- 1 zhy zhy 190 Jan 4 20:15 tmp3.zip-rw-rw-r-- 1 zhy zhy 10240 Jan 4 20:20 tmp4.tar# 解包[zhy@Centos ~]$ tar -xvf tmp4.tarhome/zhy/tmp2/home/zhy/tmp2/tmp1/home/zhy/tmp2/book15. bc指令
在Linux中,bc是一个命令行计算器工具。
它用于执行数学运算,包括基本的算术运算、逻辑运算和一些高级功能,如函数、循环和条件语句。使用bc可以在终端中进行数值计算,也可以在脚本中嵌入进行数学计算操作。要使用bc指令,只需在终端中输入bc并按下回车键即可启动bc计算器。
[zhy@Centos ~]$ bcbc 1.07.1Copyright 1991-1994, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2004, 2006, 2008, 2012-2017 Free Software Foundation, Inc.This is free software with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.For details type `warranty'.2 + 2410 / 2516. uname –r指令
uname -r指令在Linux中用于显示操作系统的内核版本。
执行uname -r指令将输出当前系统内核的版本号。
[zhy@Centos ~]$ uname -r5.10.134-15.al8.x86_6417. 热键
几个重要的热键:
[Tab]按键—具有『命令补全』和『档案补齐』的功能[Ctrl]-c按键—让当前的程序『停掉』[Ctrl]-d按键—通常代表着:『键盘输入结束(End Of File, EOF 戒 End OfInput)』的意思;另外,他也可以用来取代exit
18. shutdown
语法:
shutdown [选项]
** 常见选项:**
-h: 将系统的服务停掉后,立即关机。
-r: 在将系统的服务停掉之后就重新启动
-t sec : -t 后面加秒数,亦即『过几秒后关机』的意思